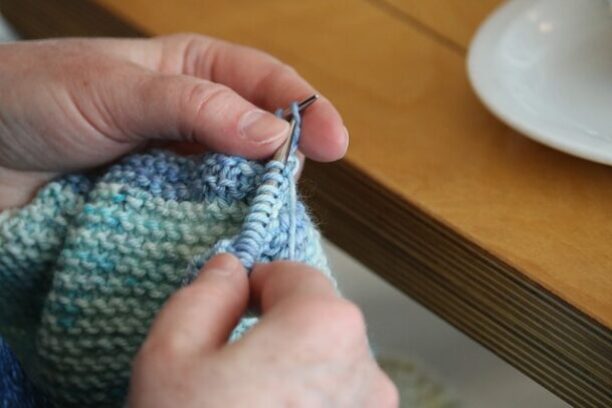
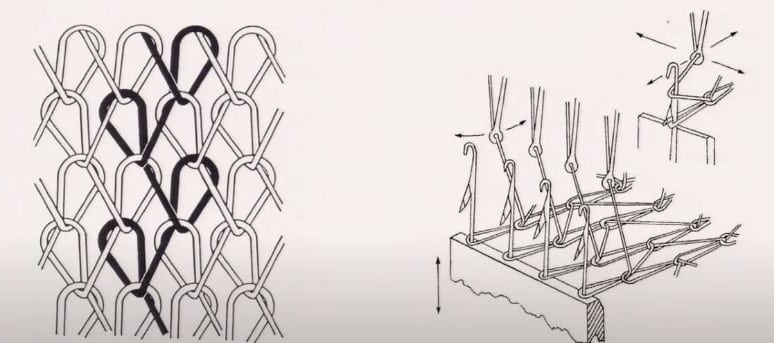
In a warp knitting process, the path of the yarn moves along the length direction, In woven technologies usually length indicates the warp direction, so that’s why this type of knitting the called warp knitting.
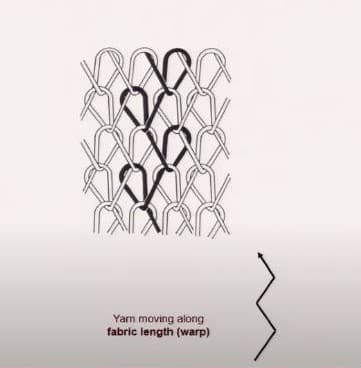
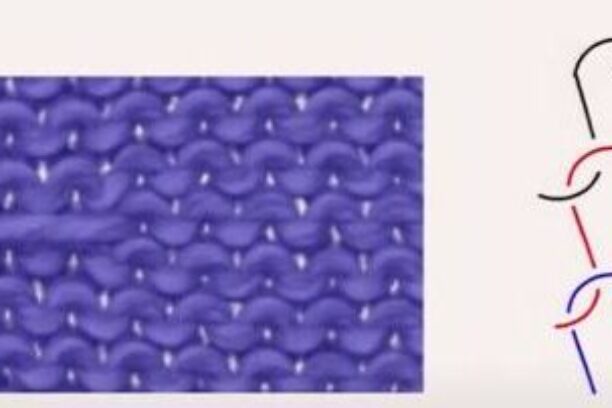
Ina warp knit structure the loops does not look like stable loops just like weft knitting, they rather have a different network of loop intermeshing, the structure of the loop is different than weft knitting. The structural possibilities are unlimited and the designs are highly complicated
Warp Knitting Process Loop formation
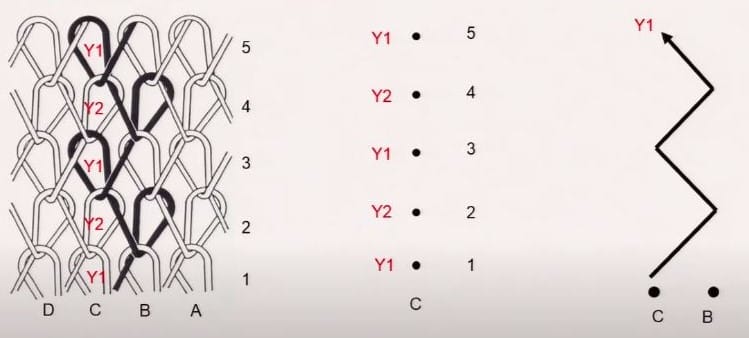
In a warp knitting process, the same needle in every alternating course is catching the different yarn. If you see the notation C in the first course catching the Y1 yarn, second-course catching Y2 yarn, the third course catching Y1 yarn, and these yarn are provided by the guide to this needle and these guides take the yarn from one needle to another needle. if you follow the path of the black yarn you can see that in alternating courses it’s shifting the position of the needle.
The second-course black yarn with needle B in the third course with needle C is repeated. The guide is taking the yarn from one needle to another needle in subsequent courses for creating the structure.
And for providing yarn to each needle we have individual guides who keep changing the location in every altering course. This is how you define a design of very simple warp structures.
The role of the guide is extremely important because the movement of the guide in the subsequent course will decide how the loops in the structure look like and what type of fabric design want to create